Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-28 Origin: Site
A diamond saw blade is a crucial tool in various industries, including construction and manufacturing. It features a steel core and diamond segments designed for tough materials like concrete and stone. The construction of the blade, including material choice, bonding matrix, and diamond quality, directly influences its performance.
In this article, we’ll explore how these elements impact cutting speed, precision, and blade lifespan. By understanding these factors, you can make informed decisions on selecting the best diamond saw blade for your specific needs.
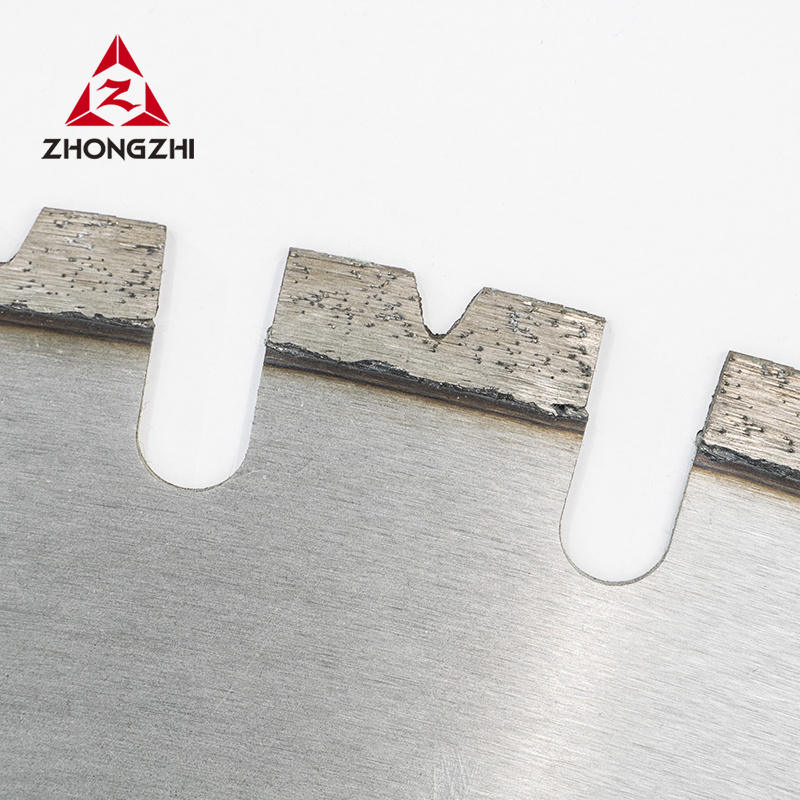
The steel core of a diamond saw blade is an integral component that provides structural integrity, support, and stability. It ensures that the blade performs well under pressure and high speeds while resisting deformation.
Material Choice: Steel is chosen for its strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear. Most diamond saw blades feature high-carbon steel or stainless steel cores that allow them to endure the stresses of high-speed rotation. The core must balance toughness and ductility, ensuring that it doesn't break or warp during cutting.
Manufacturing Process: The steel core is usually factory-tensioned, meaning it is precisely adjusted to maintain a uniform shape during cutting. Proper tensioning is crucial as it prevents the blade from warping, ensuring straight, consistent cuts. This also improves the overall stability and accuracy of the cut, particularly when cutting large or rigid materials like concrete.
The core also serves as a heat sink, dissipating the heat generated during the cutting process. If the core fails to dissipate heat effectively, the blade could overheat, reducing its lifespan and cutting efficiency.
The diamond segments are the cutting edge of a diamond saw blade. These segments contain industrial-grade synthetic diamonds that do the actual cutting of materials. They are bonded to the steel core, and the diamond particles are specifically chosen for their hardness and longevity.
Types of Diamonds Used: Synthetic diamonds are the preferred choice in modern diamond saw blades. These diamonds are engineered to provide superior performance compared to natural diamonds. Synthetic diamonds have a more uniform structure, allowing for more consistent cuts and enhanced durability.
Grit Size and Quality: The size of the diamonds and the overall quality of the diamond particles affect cutting efficiency. Finer grit diamonds are ideal for precision cuts, while larger diamonds are designed for cutting through tougher, denser materials. Higher-quality diamonds maintain sharpness longer, providing better cutting results over time.
The diamond segments are engineered to wear evenly, ensuring that fresh diamonds are constantly exposed during the cutting process. This continuous exposure is what makes diamond saw blades incredibly effective at cutting through hard materials, unlike traditional saw blades.
The bonding matrix is a critical component that holds the diamonds in place. The matrix plays an essential role in the blade's overall performance by determining how quickly new diamonds are exposed and how long they stay sharp.
Definition and Function: The bonding matrix is made from a metal powder that holds the diamonds in place. This matrix also determines how efficiently the diamonds will be exposed during cutting. As the blade rotates and grinds through materials, the bond wears away, gradually exposing new diamonds for continuous cutting.
Types of Bonds: There are two primary types of bonds used in diamond saw blades: soft and hard bonds. Soft bonds are designed for cutting harder materials like concrete and asphalt, while hard bonds are more suitable for cutting softer, more abrasive materials like tile and stone. The bond hardness must be matched to the material being cut to achieve the best cutting performance.
Soft bonds wear away more quickly, allowing new diamonds to be exposed at a faster rate, while hard bonds last longer but can become "glazed" when used on hard materials, potentially slowing the cutting process. Matching the bond type with the material being cut is essential to optimizing the blade's cutting performance and longevity.
A soft bonding matrix is essential when cutting hard, dense materials such as concrete, asphalt, or granite. The softness of the bond allows the diamond particles to be exposed quickly and continuously, ensuring efficient and rapid cutting.
Application: Diamond saw blades with soft bonds are ideal for applications where hard materials must be cut quickly and efficiently. For example, when cutting through cured concrete or dense stone, the soft bond ensures that the blade remains effective by constantly exposing fresh diamonds.
Cutting Efficiency: Soft bonds increase cutting speed by allowing new diamonds to be exposed as the old ones wear down. This continuous exposure is key to maintaining cutting performance, especially when dealing with abrasive or high-strength materials.
On the other hand, cutting softer, more abrasive materials such as tile or stone requires a harder bonding matrix. Harder bonds resist wear and tear, allowing diamonds to remain in place for a longer period.
Application: Hard bonds are well-suited for cutting softer materials like ceramics, bricks, and tiles. The hard matrix ensures that the diamonds don’t wear out prematurely while cutting through these materials, which can be less dense and more abrasive than concrete.
Impact on Blade Longevity: A harder bond extends the blade's lifespan by preventing excessive wear. However, while it reduces wear, it can also lead to slower cutting speeds compared to blades with softer bonds. Choosing the correct bond type ensures that the blade works efficiently without unnecessary premature wear.
Selecting the right bond hardness is crucial for maximizing cutting performance. Using the wrong bond type can result in inefficient cutting and reduced blade life.
Optimal Blade Selection: To optimize cutting efficiency and blade longevity, it’s important to choose the correct bond type based on the material's hardness. For example, a soft bond is ideal for tough, dense materials, while a hard bond is better suited for softer, more abrasive materials. Understanding the material being cut is essential for making the best blade selection.
The quality of the diamonds embedded in the segments of a diamond saw blade is one of the key factors that determines the blade's performance and longevity.
Performance Boost: High-quality diamonds provide better cutting efficiency and longer lifespan. These diamonds are more resistant to wear and can handle tougher materials.
Cost Considerations: While high-quality diamonds can increase the initial cost of a diamond saw blade, they are a worthwhile investment for projects requiring precision and long-lasting performance. For example, high-quality diamonds allow the blade to cut faster and more precisely, which can be essential for industrial applications.
Diamond concentration refers to the amount of diamond material present in the segments. Higher concentrations of diamonds lead to better cutting performance but require more power to operate.
High-Concentration Blades: Blades with higher diamond concentrations are more efficient at cutting through tough, dense materials like concrete and granite. The increased number of diamond particles allows for more cutting points, improving the blade's ability to grind through hard materials quickly.
Power Requirements: Blades with higher diamond concentrations generally require more horsepower to operate. The additional power allows the blade to handle the increased friction and heat generated during cutting, leading to faster and more efficient cuts.
Diamond density refers to how closely the diamond particles are packed together in the segments. Higher diamond density increases the blade’s efficiency but may affect its cutting speed.
Density Impact: Higher-density diamonds provide more contact points with the material, making the blade more efficient. However, the increased density can create more friction, which may reduce cutting speed. Balancing diamond density with material type is essential to achieving optimal cutting performance.
Segmented blades are designed with gaps between the diamond segments, making them ideal for cutting dense, tough materials like concrete, asphalt, and stone.
Use in Concrete and Asphalt: The gaps between the segments allow for better cooling during cutting, which helps to prevent the blade from overheating and ensures that the diamonds remain sharp. This design is ideal for materials that generate significant heat during cutting.
Cutting Mechanism: The segmented design helps reduce friction and allows for more efficient cutting by maintaining a clear path for the blade to move through the material. The segmented structure is essential for tackling large, dense materials.
Continuous rim blades, unlike segmented blades, feature an unbroken cutting edge. This design is perfect for cutting delicate materials like tile, ceramics, and glass.
Tile and Ceramic Cutting: The smooth, continuous rim allows for a cleaner and more precise cut, which is essential when working with fragile materials like tile or ceramics. These materials require a finer, more controlled cutting process to avoid breaking or chipping.
Finishing Quality: The continuous rim design produces a smoother cut, making it ideal for projects where the finish quality is important, such as bathroom or kitchen tiling.
The width of the diamond segments affects how the blade performs, particularly when cutting through tough materials.
Wide vs. Narrow Segments: Wider segments provide more clearance, which helps to prevent the blade from binding and allows for faster cuts. However, narrower segments can offer more flexibility and are better suited for intricate, detailed cuts.
Blade Flexibility: The width of the segments also influences the blade’s ability to handle pressure. A flexible blade is necessary when cutting irregular shapes or when working in confined spaces.
Laser welding is a popular method for attaching diamond segments to the steel core. It offers superior strength and precision, ensuring the segments stay securely in place during high-speed cutting.
Precision and Strength: Laser welding creates a strong bond between the segments and the core, preventing the segments from becoming loose or dislodged during cutting. This ensures a stable, efficient cut.
Heat Tolerance: Laser-welded blades can handle higher temperatures, making them ideal for heavy-duty cutting where heat buildup is a concern.
Other bonding methods, such as brazing and mechanical bonding, also contribute to the overall strength and durability of the blade.
Bond Strength: Brazing involves applying a silver solder layer between the segment and the core, while mechanical bonds physically lock the segments in place. Both methods offer durability, with brazing offering superior heat resistance and mechanical bonding providing strength for lighter-duty applications.
Suitability for Various Materials: Different attachment methods are better suited for different materials. Brazed and mechanical bonds can provide the necessary durability for various types of cutting jobs.
Selecting the right diamond saw blade for the material you are cutting is crucial to achieving optimal cutting performance.
| Material | Ideal Bond Type | Recommended Segment Design |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete | Soft Bond | Segmented |
| Tile | Hard Bond | Continuous Rim |
| Asphalt | Soft Bond | Segmented |
| Granite | Hard Bond | Segmented |
Matching Blade to Material: Harder materials like granite and concrete require blades with soft bonds and high-quality diamonds, while softer, more abrasive materials like tile require harder bonds.
Adjusting for Material Hardness: Choose a blade that matches the material’s hardness to ensure cutting efficiency and longevity. Always consider the specific application when selecting a blade.
Proper cutting techniques can significantly improve cutting performance and extend blade life.
Speed and Pressure: Use the right cutting speed and pressure to maximize the blade's efficiency. Excessive speed can cause overheating, while too much pressure can lead to uneven cuts.
Cooling Methods: Using water or lubrication during cutting helps reduce heat buildup and friction, ensuring the blade stays sharp and performs optimally.
Regular maintenance, including blade dressing, is essential for keeping a diamond saw blade in top condition.
When to Dress a Blade: Blade dressing should be done when the diamond segments become worn, which restores cutting efficiency by exposing fresh diamond particles.
Blade Inspection: Regularly inspect blades for signs of wear, cracks, or damage. Replacing or repairing blades when necessary will prevent subpar performance and ensure safety.
The construction of a diamond saw blade directly impacts its cutting performance, durability, and precision. Factors like the materials, bonding matrix, diamond concentration, and segment design determine how well a blade cuts through different materials. Understanding these factors helps you choose the right blade for optimal performance and longevity. By carefully selecting a blade, you can maximize its cutting efficiency and lifespan. Zhongzhi provides high-performance diamond saw blades that deliver exceptional value, ensuring top-notch results for the toughest tasks.
A: The blade's construction, including the material of the steel core, diamond concentration, and bonding matrix, directly affects cutting speed, precision, and lifespan.
A: A diamond saw blade with a soft bonding matrix is ideal for cutting hard materials like concrete and granite, as it allows for quick diamond exposure.
A: The bonding matrix holds the diamonds in place and determines how quickly new diamonds are exposed, influencing cutting efficiency and blade durability.
A: Higher diamond concentration increases cutting efficiency and durability, but it requires more power and can reduce cutting speed.
A: Yes, but a diamond saw blade with a hard bonding matrix and continuous rim design is recommended for cutting delicate materials like tile for smoother results.

